Forget the 7:1 Rule – Your Dog's Age May Be Much Higher Than You Think
Introduction
For years, the common belief was that one dog year is equivalent to seven human years, a rule of thumb many pet owners used to estimate their furry friend's age. However, recent scientific research has revealed that this popular notion may be far from accurate. The age of your dog could be much higher than you previously thought, and it's time to forget the old 7:1 rule. A study conducted at the School of Medicine of the University of California, San Diego, challenges the traditional wisdom, suggesting that the aging process in dogs and humans is more complex than a simple numerical ratio.
The Flaw in the 7:1 Rule
The 7:1 rule was a straightforward way of calculating a dog's age compared to human years. However, it failed to consider the variations in the rate of aging throughout a dog's life. Professor Trey Ideker, a prominent figure in the field, pointed out the fallacy of this conventional rule. He explained that a nine-month-old puppy can give birth to a litter, indicating that the 7:1 ratio is an inaccurate measure of aging. The study aimed to provide a more accurate understanding of the relationship between canine and human aging.
The Research Methodology
To arrive at their groundbreaking conclusions, researchers analyzed blood samples from 105 Labrador Retrievers. The goal was to examine the genetic markers in these dogs and compare them to human genetics. The study found that dogs age more rapidly than humans during their early years, with the aging process gradually slowing down as they grow older. This fundamental finding challenges the simplicity of the 7:1 ratio and suggests that aging is a more intricate process than previously thought.
The New Understanding of Canine Age
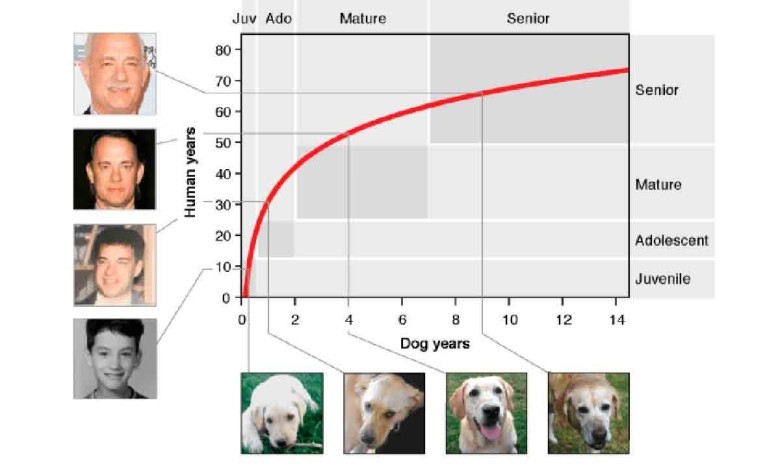
The study offered a more nuanced approach to calculating a dog's age in human years. Rather than relying on a one-size-fits-all rule, the research indicates that the age of a dog can vary considerably based on its life stage. The following observations were made:
-
Puppyhood: During the early months of a dog's life, it ages very quickly compared to humans. Researchers found that the first year of a dog's life is approximately equivalent to 30 human years, highlighting the rapid growth and development that takes place in a short period.
-
Young Adulthood: As dogs reach their second year, their aging process begins to slow down. It is estimated that dogs age about 4 human years for every dog year during this stage.
-
Middle Age: The slowing of aging continues, and by the time a dog reaches its seventh year, the aging process has significantly decelerated. This stage can be compared to a human in their fifties.
-
Senior Years: Beyond the age of seven, dogs continue to age more slowly, and the rate of aging becomes less linear. A twelve-year-old dog, for example, is roughly equivalent to a seventy-year-old human.
Implications for Veterinary Care
Understanding the true age of a dog can have substantial implications for veterinary care and overall pet wellness. The new model of aging allows veterinarians to make more accurate assessments of a dog's health based on its biological age, rather than simply relying on chronological age. This means that veterinarians can better identify potential health issues and provide tailored care for older dogs, even if they fall short of the traditional 7:1 ratio.
Furthermore, the study's findings may also be beneficial for pet owners. They provide a more accurate perspective on their dog's aging process and enable them to make informed decisions about their pet's care and well-being.
Conclusion
The traditional 7:1 rule for calculating a dog's age in human years has been challenged by scientific research. The study conducted at the University of California, San Diego, revealed that the aging process in dogs is more complex and varies significantly throughout their life stages. Understanding a dog's true age, rather than relying on a fixed ratio, can lead to better veterinary care and enhanced overall pet wellness.
This new perspective not only contributes to more accurate health assessments but also underscores the uniqueness of the bond between humans and their canine companions. It allows pet owners to appreciate their dogs at each stage of life and to provide them with the care and attention they deserve. So, the next time you look at your furry friend, remember that their age may be quite different from what you previously thought, and their journey through life is even more remarkable.













Comments
0 comment