views

- Patient Presents with Pitting Swelling in Both Legs and Frothy Urine: Diagnosis
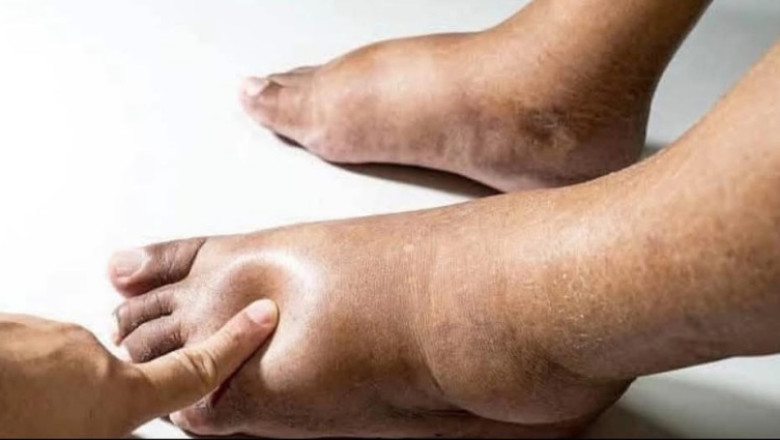
A patient arrives at the clinic with complaints of pitting edema in both legs and frothy urine. The patient describes the swelling as persistent and noticeable, particularly towards the end of the day. The frothy urine is a recent development, and the patient is concerned about its implications.
Clinical Presentation
The primary symptoms of the patient are:
-
Pitting Edema: The patient presents with noticeable swelling in both legs, which leaves an indentation when pressure is applied. The swelling is more pronounced in the evening and after prolonged periods of standing or sitting.
-
Frothy Urine: The patient reports observing frothy or bubbly urine, which is unusual for them. The frothiness is consistent and not just a one-time occurrence.
Differential Diagnosis
Given the patient's symptoms, several potential diagnoses should be considered:
-
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD): Pitting edema and frothy urine can be indicative of kidney dysfunction, where the kidneys are unable to filter waste and excess fluid effectively.
-
Nephrotic Syndrome: This condition is characterized by significant proteinuria (excess protein in the urine), leading to frothy urine and edema due to fluid retention.
-
Heart Failure: Congestive heart failure can cause fluid buildup in the lower extremities and lead to pitting edema. The reduced cardiac output can also affect kidney function, resulting in frothy urine.
-
Liver Disease: Liver cirrhosis can lead to fluid retention and pitting edema. The impaired liver function can also affect the kidneys, causing proteinuria and frothy urine.
-
Proteinuria: Excess protein in the urine can cause frothy urine and may be associated with underlying kidney conditions.
Diagnostic Workup
To determine the underlying cause of the patient's symptoms, the following diagnostic tests and evaluations are recommended:
-
Urine Analysis: To check for proteinuria and other abnormalities in the urine.
-
Blood Tests: To assess kidney function (e.g., serum creatinine, blood urea nitrogen) and liver function (e.g., liver enzymes, bilirubin).
-
Imaging Studies: Ultrasound of the kidneys and liver to evaluate for structural abnormalities.
-
Echocardiogram: To assess cardiac function and rule out heart failure.
-
Kidney Biopsy: In cases where nephrotic syndrome or other kidney diseases are suspected, a biopsy may be necessary to determine the exact cause.
Conclusion
The patient's presentation with pitting edema in both legs and frothy urine necessitates a thorough diagnostic workup to ascertain the precise cause. Early diagnosis and appropriate therapeutic intervention are crucial for managing the condition and preventing potential complications. Regular follow-up and monitoring are indispensable to ensure the patient's overall health and well-being.











Comments
0 comment